Showroom
There are different between drugs and medicines. Medicines are general whereas drugs are more advanced in treating numerous diseases. Our pharmaceutical drugs are used to treat cancer, diseases, persistent side effects and more. Well planned and formulated drugs help patients in pain free and least symptoms method. Lead precious smooth life through our drugs to cure your problems.
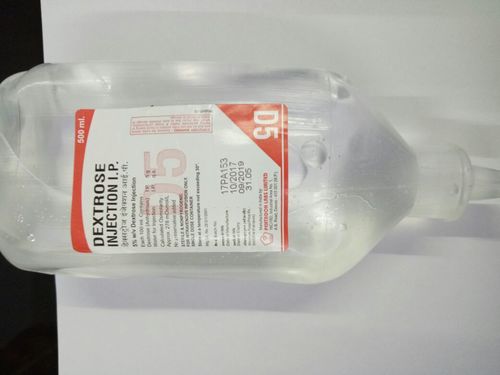
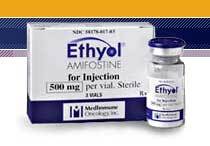
When any disease seems running out of control or requiring injectables, then our pharmaceutical injectables are deployed for peoples welfare. These are primarily generic drugs that are able to directly injected in patients body, mainly deployed in curing critical illnesses. They are impeccably composed, cleaned and stored, therefore, they are ready to deploy injectables.
Our antibiotic drugs, additionally called anti-bacterial, are a kind of antimicrobial medication deployed in prevention and treatment of bacterial diseases. These may either stop bacteria development or kill bacteria. A set number of our drugs additionally have antiprotozoal activity. Our drugs are strong in nature that combats infections in body.
Offered generic drugs are duplicates of brand-name sedates that have the very same dose, planned applications, impacts, symptoms, administration route, dangers, protection and power as the authentic medication. As such, their pharmacological impacts are precisely similar as those of their authentic name counterparts.
Our pharma medicine is profited by numerous pharmaceutical stores for simple medicinal access to the customers. Many a times, diseases can be cured at home without spending much money in doctors appointments. Nevertheless, our medicine comes in tablets, capsules, gels, liquids and more to be used as per patients inclination.
Cancer is something that scares all of us only through its name. But to many people, it is life changing phase because major medical deaths have been occurred by it. Therefore, our anti cancer injections are introduces to stop and reduce the cancer cells development in the body to offer relief from grave diseases.
Our chemotherapy is the utilization of any medication to cure any sickness. Yet to countless people, the name chemotherapy implies drugs utilized for treatment of cancer. It's frequently abbreviated to "chemo." Radiation therapy and surgery damage, kill or remove cancer cells in specific area, yet chemo can work all through the entire body.
The kidneys are fundamental organs that individuals use to dispose of additional waste as well as water from their blood. Kidneys likewise help control our circulatory strain. Individuals can lessen their danger of growing and eliminating kidney cancer by keeping up sound way of life and prescription of our kidney cancer drugs.
Our anti psychiatric drugs are acknowledged as psychotropic drugs that are utilized as a transient therapy for bipolar disorder to direct maniacal side effects, for example, mania, delusions or mental trips side effects. These side effects may happen amid intense insanity or extreme depression. But, no worries, our drugs help patients effectively.
Our oncology medicine helps general population, who are encountering distinguished kinds of cancer. Offered medicine is well formulated and developed that helps in its proper functioning through curing cancers in danger safe manner. Doctors suggest our medicine to patients to treat pancreas cancer, intestinal cancer, kidney cancer and different other cancers.
Trigger point injection is synonym of our anesthesia medicine that is employed by patients and doctors to offer relief to pain that is connected with body muscles. Mainly, our medicine is employed by numerous health care specialists to induce or maintain unconsciousness in surgery sans taking any danger regarding patients health and life.
To put trust in doctors is easy rather than some bought medicines. Yet in truth, medicine is friend of doctors that helps patients to get back on sound health track in short period. Our anti cancer tablets are precisely composed with nil side effects. In addition, for quick relief in cancer pain, doctors recommend the deployment of our tablets.
Our vaccines are biological formulations that offer active obtained immunity to a specific disease. These include a specialist that imitates a disease inducing microorganism. In addition, our injections are composed from killed or weakened kinds of microbe, one from its surface proteins or its toxins. Patients can cure their disease through our provided injections at once.
Major diseases are induced by viruses that have practically succumbed to our virology drugs for measles, polio, yellow fever, small pox and more. In addition, chronic infections can be treated through our drugs after acquiring prescription from health care specialists. Offered drugs are equivalent to expensive treatments, therefore, users can trust them without hesitation.
Breast cancer is the most dangerous disease among ladies and yet most of them truly do not comprehend much about the disease. The risk increases among those women who have grandmother, sister, aunt or mother who has the disease much before age 50. However, our breast cancer drugs cures every stage of cancer in women.
Precious thing to live longer is factually not water. Then whats important? Your blood is precious for your longer life. But sometimes, blood cancer strikes most of us earlier, later or never. Therefore, if you need to treat your blood cancer in simplest manner then avail our blood cancer drugs, as we care for life!
Prostate cancer grow in an organ of male reproductive system. The cancer is moderate developing, nevertheless, some develop generally rapidly. In addition, the cells may increase from prostate to different body parts. Therefore, introduction of our prostate cancer drugs is initiated to help patients economically and effectively for their happy times.
If customers encounter heart attack then they will most possibly be suggested medicines or drugs that they will consume for their remaining life. However, through our cardiac drugs many issues can take turn back to sound heart health. Our drugs inhibits the causes of cardiac problems in best approach ever formulated.
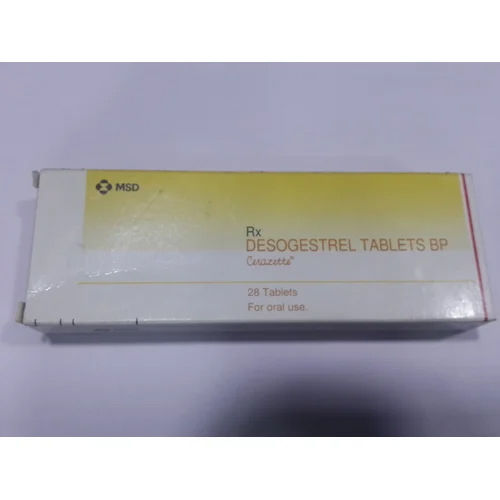
Provided gynecology medicine is deployed to analyze the women and men fertility, delayed puberty, androgen deficiency and more issues that comes in ongoing as well as future pregnancies. It removes or nullifies any cause amid abortion, pregnancy or any mishap that may lead to excess bleeding through placenta. Our medicine also helps in treating side effects such as eye dryness, soreness, irritation or burning.
Diabetes portrays a class of metabolic infections in which the individual has elevated blood glucose, either due to insulin generation is deficient or cells of body do not react appropriately to insulin or may be both. Hence, our anti diabetic medicines help patients to get rid of diabetic issues in ease manner.
Our dermatology products as tittle states are mainly formulated to cure skin related problems of general people. Skin problems are more frequent in people of every age. Some problems are acute that require occasional medications to control the problem. Our provided products are for all, which implies every age group can simply deploy our medicines as per doctors recommendation.
Now a days, infertility is persistent not only in women but men also. To overcome this issue, individuals are opting for long medical treatment that does not assure them fertility. Therefore, our infertility drugs have been introduced to eliminate the cause of infertility. Our drugs helps in making individuals life cheerful again.
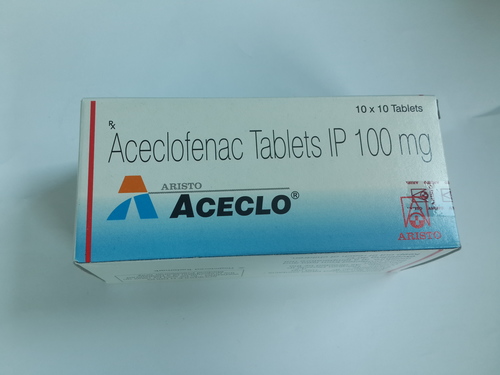
Our pharmaceutical tablets offer effective solutions for various medical conditions. From pain relief to chronic disease management, our tablets are meticulously formulated to deliver precise dosages and consistent results. Each tablet undergoes rigorous quality control measures to ensure safety and efficacy. With our diverse range of pharmaceutical tablets, you can trust us to provide reliable solutions for your healthcare needs.
Our anti-cancer drugs are meticulously developed to target and combat cancer cells effectively. With advanced formulations and rigorous testing, our medications offer hope and support to patients battling cancer. Each drug is designed to minimize side effects and maximize therapeutic benefits, providing patients with the best possible chance of remission and improved quality of life. Trust our anti-cancer drugs for comprehensive and compassionate cancer care.
Our pharmaceutical medicines encompass a wide range of treatments for various health conditions. From common ailments to complex diseases, our medications are formulated to provide effective relief and support. Each medicine undergoes stringent quality checks to ensure safety and efficacy. With our diverse portfolio of pharmaceutical medicines, you can trust us to deliver high-quality solutions for your healthcare needs.
Our pharmaceutical products encompass a comprehensive range of medications and healthcare solutions. From prescription drugs to over-the-counter remedies, our products are designed to meet diverse medical needs. With a focus on quality and efficacy, each product undergoes rigorous testing and adheres to stringent regulatory standards. Whether you require medications, supplements, or medical devices, trust our pharmaceutical products to deliver safe and effective solutions for your health and wellness needs.
Our antibiotic medicines offer effective treatment for bacterial infections, helping patients recover quickly and safely. With a wide range of formulations and strengths, our antibiotics target various types of bacteria to combat infections effectively. Each medication is rigorously tested for potency and safety, ensuring reliable results and minimal side effects. Trust our antibiotic medicines to provide the essential support needed to fight bacterial infections and restore health.
Our vaccines drugs offer essential protection against a variety of infectious diseases, providing immunity and preventing outbreaks. Developed using cutting-edge technology and stringent quality control measures, our vaccines are safe, effective, and recommended by healthcare professionals worldwide. From childhood immunizations to travel vaccines, we offer a comprehensive range of products to safeguard individuals and communities against preventable diseases. Trust our vaccines drugs for reliable and long-lasting immunity.
Our diabetic drugs are specifically formulated to help manage blood sugar levels and control symptoms associated with diabetes. With a focus on efficacy and safety, our medications offer reliable support for individuals living with diabetes. From oral medications to injectables, our diverse range of diabetic drugs provides options tailored to individual needs. Trust our diabetic drugs to help you maintain optimal health and wellness while managing diabetes effectively.
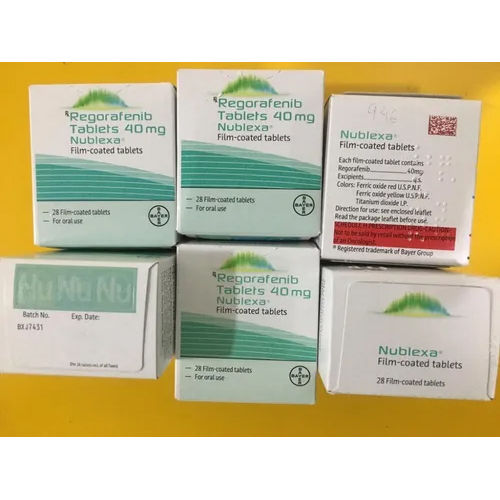
Regorafenib Tablets 40mg are a targeted therapy used to treat certain types of cancer. As an oral medication, these tablets work by inhibiting the growth and spread of cancer cells in the body. Often prescribed for advanced colorectal cancer and gastrointestinal stromal tumors, regorafenib tablets offer hope and support to patients battling cancer. Trust this medication as part of your comprehensive cancer treatment plan.
Our cancer treatment tablets are specifically formulated to combat various types of cancer effectively. These tablets target cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells, offering patients a chance at remission and improved quality of life. With advanced formulations and rigorous testing, our cancer treatment tablets provide hope and support to individuals fighting cancer. Trust our medications to be an integral part of your cancer treatment journey.
Our asthma inhaler is a vital tool for managing asthma symptoms and providing quick relief during flare-ups. With a metered-dose design, it delivers a precise dose of medication directly to the lungs, helping to open airways and alleviate breathing difficulties. Compact and easy to use, our asthma inhaler offers convenience and peace of mind for individuals living with asthma. Trust it to provide effective symptom relief whenever needed.
Our active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are the cornerstone of pharmaceutical formulations, providing the therapeutic effects essential for treating various medical conditions. Meticulously sourced and manufactured, our APIs adhere to stringent quality standards, ensuring safety, efficacy, and consistency in every dosage form. With a diverse range of APIs available, we are committed to supplying pharmaceutical manufacturers with high-quality ingredients to produce superior medications.
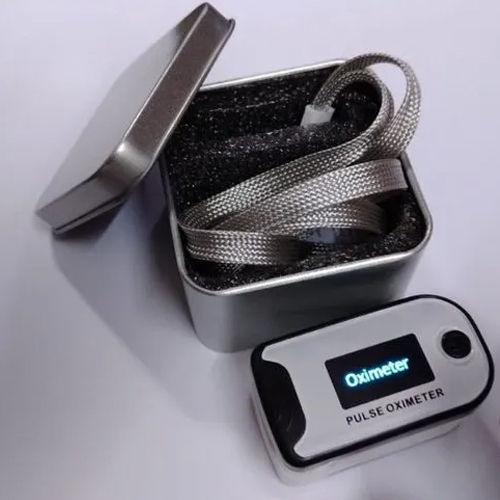
Our fingertip pulse oximeter is a portable and convenient device for monitoring oxygen saturation levels and heart rate. With its simple fingertip application and easy-to-read display, it provides accurate readings within seconds. Ideal for home use or clinical settings, our pulse oximeter offers peace of mind by allowing users to track their health status quickly and effectively. Trust it to provide reliable measurements whenever and wherever needed.
Our nutrition supplement is a comprehensive blend of essential vitamins, minerals, and nutrients designed to support overall health and well-being. Formulated with premium-quality ingredients, it provides the body with the necessary nutrients to maintain optimal function and vitality. Whether used as a daily supplement or to address specific nutritional deficiencies, our product offers a convenient and effective way to support a healthy lifestyle. Trust it to fuel your body with the nutrients it needs.
"Accepting orders in bulk order quantity".
 |
DHEER HEALTHCARE PRIVATE LIMITED
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese